Regression testing is a key follow to forestall modifications for bringing unfavorable side-effects in manufacturing. Operating them may nevertheless take a very long time and gradual supply of recent code. This text introduces change-to-test mapping for regression testing. It’s an method that goals to run solely the checks that really matter, with out compromising take a look at protection.
Creator: Yulia Drogunova, https://www.linkedin.com/in/yulia-drogunova-409703113/
Introduction
Regression testing is important to software program high quality, however in enterprise initiatives it typically turns into a bottleneck. Full regression suites could run for hours, delaying suggestions and slowing supply. The issue is sharper in agile and DevOps, the place groups should launch updates each day.
This text introduces change-to-test mapping – a sensible method that runs solely the checks that really matter, with out compromising protection. By specializing in relevance as an alternative of quantity, organizations can speed up supply whereas sustaining confidence.
As take a look at suites develop in dimension and complexity, masking not solely purposeful checks but in addition integration, API, efficiency, and safety, smarter choice methods have gotten a necessity somewhat than an optimization.
Why Now?
The necessity for smarter regression methods is extra pressing than ever. Fashionable software program programs are not monoliths; they’re constructed from microservices, APIs, and distributed parts, every evolving rapidly. Each code change can ripple throughout modules, making full regressions more and more impractical. On the similar time, CI/CD prices are rising sharply. Cloud pipelines scale simply however generate large payments when regression packs run repeatedly. For a lot of organizations, testing has change into one of many largest operational bills in supply.
The Regression Strain
In lots of initiatives, even a minor code change could set off tons of or 1000’s of automated checks. This creates:
- Lengthy-running CI/CD pipelines
- Delayed suggestions for builders
- Bottlenecks in supply workflows
In industries similar to banking, e-commerce, and telecom, regression packs can simply develop into tens of 1000’s of checks – turning each launch right into a pricey and time-consuming course of. Past price and time, extreme regressions additionally have an effect on workforce conduct: builders could keep away from operating checks domestically, hotfixes could be delayed as a consequence of lengthy validation cycles, and product managers could hesitate to roll out incremental updates. What ought to be a safeguard typically turns into a bottleneck, limiting innovation and slowing time-to-market.
Change-to-Take a look at Mapping: A Pragmatic Method
The core concept is straightforward: “If solely a part of the code modifications, why not run solely the checks masking that half?”
Change-to-test mapping hyperlinks modified code to the related checks. As a substitute of operating the complete suite on each commit, the method executes a focused subset – whereas retaining safeguards similar to security checks and fallback runs.
What makes this method pragmatic is that it doesn’t depend on constructing a “good” mannequin of the system. As a substitute, it makes use of light-weight indicators – similar to file modifications, annotations, or protection knowledge – to approximate essentially the most related set of checks. Mixed with guardrails, this creates a stability: quick sufficient to maintain up with fashionable supply, but protected sufficient to belief in production-grade environments.
How It Works in Observe
A. Basis (arrange as soon as, maintain up-to-date)
Earlier than selective execution, keep a mapping between code modules and checks. In CodeMapRT that is completed through:
- Annotations/metadata in checks (e.g., @CoversModule(“auth”))
- Configuration information that outline module→take a look at relationships
- Protection knowledge displaying exercised information
Deal with the mapping as core infrastructure: versioned, reviewed, and up to date because the system evolves.
B. Runtime Stream (per commit/PR)
When a commit or pull request is submitted, CodeMapRT performs the next steps:
- Detect which information or modules had been modified (e.g., through Git diffs).
- Choose the checks mapped to these modules (through annotations, protection knowledge, or configuration).
- Add security checks – outlined in a devoted checklist (e.g., safety-tests.txt) and at all times included on prime of mapped checks. These cowl vital enterprise flows similar to authentication, funds, and integrations, guaranteeing important paths are validated even when solely a subset of the suite runs.
- Run the filtered suite in CI/CD.
- Use fallback full regression for main milestones.
This hybrid mannequin balances effectivity with reliability.
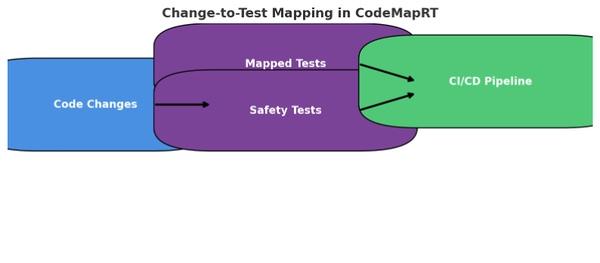
Instance of mapping code modifications to mapped and security checks in CodeMapRT earlier than execution in CI/CD.
A number of methods can additional strengthen the method:
- Static evaluation instruments (e.g., SonarQube, Semgrep) could possibly be used to establish oblique dependencies that is probably not apparent from Git diffs alone.
- Dynamic protection monitoring throughout take a look at execution would possibly constantly replace the mapping, guaranteeing that newly added or refactored checks are mechanically linked to related modules.
- Threat-based prioritization can doubtlessly be layered on prime of mapping, in order that checks related to high-criticality modules (e.g., funds, authentication, healthcare knowledge) are at all times executed first, no matter change dimension.
- Parallel execution in CI/CD would permit even a filtered suite to finish in minutes, by scaling throughout distributed runners.
- Integration with fashionable orchestration platforms (GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, Jenkins pipelines) may assist embed change-to-test mapping seamlessly into current workflows.
- Incremental adoption technique could also be a sensible path ahead: beginning with much less vital modules and step by step extending to mission-critical areas as confidence grows.
Such enhancements exhibit how change-to-test mapping can develop right into a complete method that balances effectivity with confidence in software program high quality.
Actual-world Illustration
To validate the method, a demo undertaking with 50 automated checks was created.
- Full regression: 50 checks executed on each commit
- Selective regression with mapping: 28 mapped checks + 5 security checks = 33 complete
- Final result: a 34% discount in executions, even in a small-scale demo
Even in a modest setup, this reveals measurable financial savings. In enterprise environments with 1000’s of checks, the place solely a fraction of the codebase modifications per commit, change-to-test mapping can reduce 70-90% of pointless executions – saving hours of pipeline time and decreasing CI/CD prices considerably.
Advantages in Observe
- Accelerates suggestions loops → outcomes arrive in minutes, not hours, enabling builders to validate modifications throughout the identical working session somewhat than ready for in a single day builds.
- Cuts infrastructure waste → leaner pipelines and smaller CI/CD payments, as solely related subsets of checks are executed. That is particularly precious in cloud-based environments the place each additional minute of compute interprets into direct prices.
- Helps frequent releases → regression not blocks each day supply, aligning testing with fashionable Agile and DevOps practices that demand a number of deployments per day.
- Maintains confidence → security checks and fallback runs forestall missed points, guaranteeing that protection just isn’t sacrificed for velocity. Groups retain the power to run full suites when enterprise threat is excessive.
- Scales to enterprise programs → adaptable to massive, complicated codebases with 1000’s of providers and dependencies, making it appropriate for industries like banking, telecom, and healthcare.
- Improves developer productiveness → much less ready on pipelines means extra time spent constructing options, fixing points earlier, and decreasing context-switching.
- Helps sustainability objectives → decreasing redundant take a look at executions additionally lowers vitality consumption in massive CI/CD clusters, contributing to greener IT operations.
- Delivers measurable financial savings → for instance, in a company with 10,000 automated regression checks, decreasing execution quantity by simply 50% can save tons of of hours of machine time every month, translating into each price financial savings and sooner launch cycles.
Greatest Practices & Concerns
- Begin small, scale step by step → start with one module or service to validate the method earlier than extending it throughout the complete system.
- Outline clear possession → be sure that groups know who maintains the mapping metadata (e.g., QA, builders, or a shared DevOps operate). With out possession, mappings threat changing into outdated.
- Automate mapping updates → combine protection instruments or static evaluation to maintain test-to-code hyperlinks present, decreasing the necessity for guide upkeep.
- Monitor accuracy constantly → observe false negatives (missed checks) and false positives (pointless executions) to refine the technique and enhance belief.
- Steadiness velocity with security → keep insurance policies for when to set off full regressions, similar to earlier than main releases or after high-risk architectural modifications.
- Leverage analytics → collect metrics on take a look at execution time, skipped checks, and defect leakage to measure ROI and exhibit enterprise worth.
- Put together cultural alignment → educate builders and QA groups on how selective regression works so that they belief the outcomes and don’t default to full runs “simply in case.”
- Plan for integration with different practices → mix change-to-test mapping with methods like take a look at impression evaluation, flaky take a look at detection, and parallel execution to maximise effectivity.
Conclusion
Regression testing doesn’t should be an unavoidable slowdown. By mapping code modifications to related checks, groups can speed up supply whereas preserving confidence in high quality. As take a look at suites proceed to develop, approaches like change-to-test mapping shall be key to balancing velocity, price, and high quality in software program supply.
QA groups can begin experimenting with change-to-test mapping in smaller initiatives and step by step develop adoption to bigger pipelines. Even partial implementation – similar to introducing light-weight annotations or selective take a look at triggers – can already present measurable financial savings and shorten suggestions loops. Over time, organizations can evolve these practices into a strong technique that scales to 1000’s of checks throughout enterprise programs.
The long-term potential is important: decreased operational prices, improved developer productiveness, and a sustainable testing course of that retains tempo with agile and DevOps supply fashions. As testing complexity continues to rise, selective and clever approaches is not going to solely be helpful however important for aggressive benefit.
As an open-source implementation of this concept, I created CodeMapRT, which demonstrates how change-to-test mapping could be utilized in actual CI/CD environments. It serves as each a proof of idea and a sensible software that groups can adapt, prolong, and combine into their very own pipelines – serving to to reshape regression testing right into a driver of velocity somewhat than a supply of delay.
GitHub Repository: https://github.com/yuliadrogunova/codemaprt
Concerning the Creator
Yulia Drogunova is a a Senior QA Engineer with intensive expertise in FinTech and enterprise programs. She created CodeMapRT, a framework for change-to-test mapping that streamlines regression testing. Yulia publishes articles, contributes to QA innovation, and engages in skilled communities to advertise fashionable approaches in software program testing, automation, and high quality assurance.

