Two malicious NPM packages posing as WhatsApp growth instruments have been found deploying harmful data-wiping code that recursively deletes information on a developer’s computer systems.
Two malicious NPM packages at present out there within the registry goal WhatsApp builders with harmful data-wiping code.
The packages, found by researchers at Socket, masquerade as WhatsApp socket libraries and have been downloaded over 1,100 occasions since their publication final month.
Regardless of Socket having filed takedown requests and flagging the writer, nayflore, each stay out there on the time of writing.
The names of the 2 malicious packages are naya-flore and nvlore-hsc, although the identical writer has submitted extra on NPM, like nouku-search, very-nay, naya-clone, node-smsk, and @veryflore/disc.
Though these extra 5 packages aren’t at present malicious, excessive warning is suggested, as an replace pushed at any time may inject harmful code.
All these packages mimic professional WhatsApp developer libraries used for constructing bots and automation instruments across the WhatsApp Enterprise API.
Socket notes that these libraries have not too long ago skilled a big surge in demand, as extra companies make the most of WhatsApp’s Cloud API for buyer communication.
Wiper code
Each naya-flore and nvlore-hs include a perform referred to as ‘requestPairingCode,’ that’s purported to deal with WhatsApp pairing, however which retrieves a base64 JSON file from a GitHub handle.
The JSON file accommodates a listing of Indonesian cellphone numbers that act as a kill swap, excluding homeowners of those numbers from the malicious performance.
For the remaining (legitimate targets), the code executes the ‘rm -rf *’ command, which deletes all information recursively within the present listing, successfully wiping code from the developer’s system.

Supply: Socket
Socket additionally found a dormant knowledge exfiltration perform (‘generateCreeds’), which may exfiltrate the sufferer’s cellphone quantity, system ID, standing, and hardcoded key. This perform is current however commented out in each packages, so it is disabled.

Supply: Socket
Go ecosystem hit too
In parallel information, Socket additionally found 11 malicious Go packages that use string-array obfuscation to silently execute distant payloads at runtime.
These packages spawn a shell, fetch a second-stage script or executable from .icu or .tech domains, and run it in reminiscence, concentrating on each Linux CI servers and Home windows workstations.
Nearly all of the packages are typosquats, that means they guess on developer mis-types and confusion to trick them into downloading them.
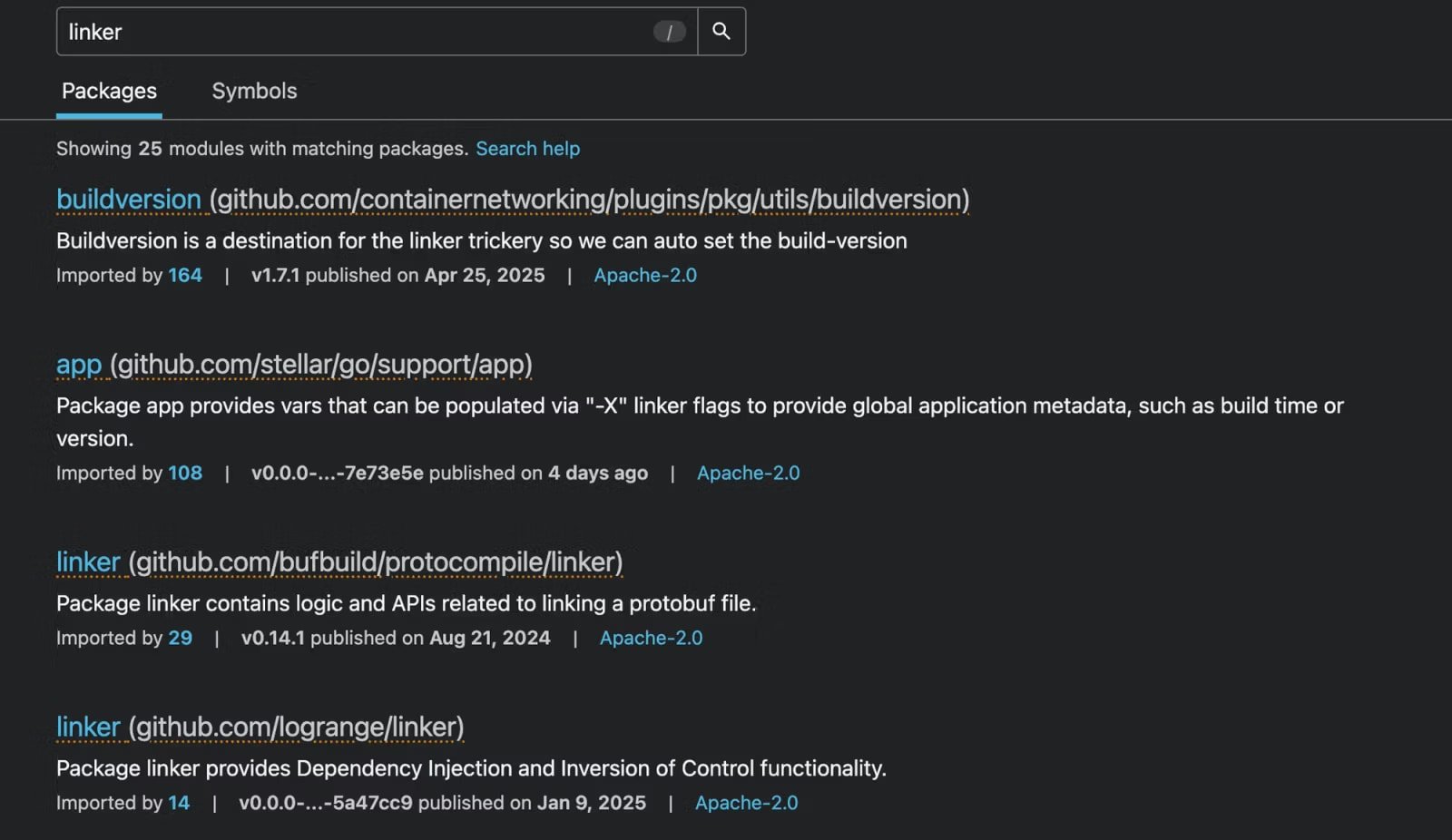
Supply: Socket
The malicious packages and their areas are listed under:
- github.com/stripedconsu/linker
- github.com/agitatedleopa/stm
- github.com/expertsandba/decide
- github.com/wetteepee/hcloud-ip-floater
- github.com/weightycine/replika
- github.com/ordinarymea/tnsr_ids
- github.com/ordinarymea/TNSR_IDS
- github.com/cavernouskina/mcp-go
- github.com/lastnymph/gouid
- github.com/sinfulsky/gouid
- github.com/briefinitia/gouid
Most of them are nonetheless reside, so Go builders are suggested to be very cautious and double-check their constructing blocks earlier than utilizing them of their environments.


