Researchers on the Massachusetts Institute of Know-how (MIT) have created MagMix, a compact magnetic system that actively prevents cell settling throughout 3D bioprinting, producing extra uniform and practical tissues. The innovation addresses a key limitation in biofabrication: sedimentation in bioinks—a combination of dwelling cells and hydrogels—which might trigger clogging, uneven cell distribution, and inconsistent tissue high quality, making it troublesome to print giant or complicated tissues reliably.
The mission acquired help from MIT’s Security, Well being, and Environmental Discovery Lab (SHED), which offers technical infrastructure and interdisciplinary experience for scaling lab improvements. “MagMix is a robust instance of how the appropriate mixture of technical infrastructure and interdisciplinary help can transfer biofabrication applied sciences towards scalable, real-world affect,” says SHED founding director Tolga Durak.
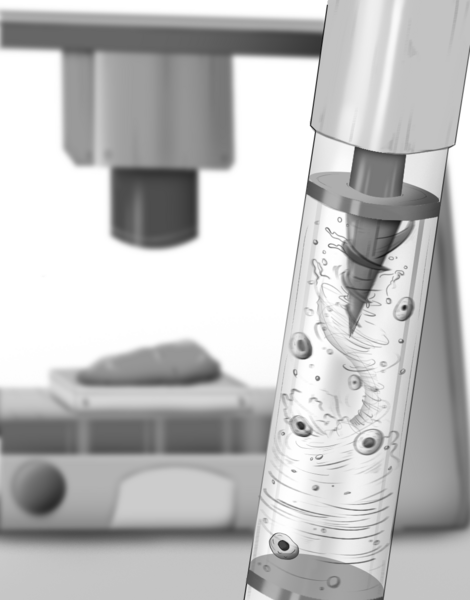
A New Method: Energetic Magnetic Mixing
In a research revealed February 2, Ritu Raman, Eugene Bell Profession Improvement Professor of Tissue Engineering at MIT, and her staff describe a way that actively prevents cell sedimentation throughout printing, making certain extra constant and biologically viable tissues. “Exact management over the bioink’s bodily and organic properties is important for recreating the construction and performance of native tissues,” says Ferdows Afghah, a postdoc in mechanical engineering at MIT and lead creator of the research.
MagMix consists of a small magnetic propeller positioned inside normal printer syringes and a motor-driven everlasting magnet exterior. This compact setup will be connected to any standard 3D bioprinter, making certain bioinks stay evenly blended all through printing with out altering their composition or affecting the printer’s normal features. The researchers first used pc simulations to find out the best propeller form and rotation velocity, after which confirmed its effectiveness by experimental checks.
“Throughout a number of bioink sorts, MagMix prevented cell settling for greater than 45 minutes of steady printing, decreasing clogging and preserving excessive cell viability,” says Raman. “Importantly, we confirmed that mixing speeds might be adjusted to stability efficient homogenization for various bioinks whereas inducing minimal stress on the cells. As a proof-of-concept, we demonstrated that MagMix might be used to 3D print cells that might mature into muscle tissues over the course of a number of days.”
Purposes in Medication and Past
By conserving cells evenly distributed, MagMix permits manufacturing of higher-quality tissues with constant organic operate. Its compact, customizable design makes it suitable with current 3D printers, providing an accessible resolution for laboratories and corporations engaged on illness modeling, drug testing, and regenerative medication.
The staff additionally sees potential past healthcare. Printed muscle tissue may energy safer and extra environment friendly biohybrid robots, whereas regenerative medication purposes purpose to interchange diseased or injured tissues with 3D printed constructs that restore wholesome operate.
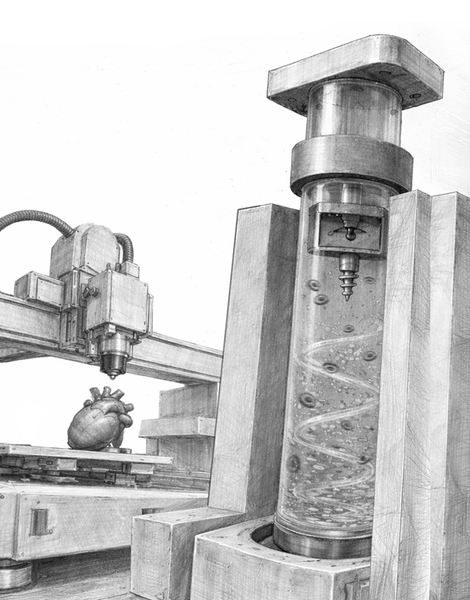

Limits and Challenges
Whereas MagMix improves cell distribution, it doesn’t eradicate all sources of variability in 3D bioprinting. Its effectiveness has been validated for as much as 45 minutes of steady printing and throughout a number of bioinks, however longer classes or untested formulations might behave otherwise. The system maintains homogeneity throughout the syringe however doesn’t tackle downstream tissue maturation, vascularization, or integration in dwelling organisms. Moreover, scaling to industrial or medical manufacturing would require additional validation, standardization, and regulatory approval earlier than it may be utilized in therapeutic or industrial settings.
Addressing Bioprinting Challenges
Sustaining even cell distribution in bioinks is among the greatest challenges in 3D bioprinting, immediately affecting tissue high quality and reproducibility. Apart from MIT, researchers are tackling this by excessive cell‑density bioinks that help stem cells in forming steady cartilage and bone areas, enhancing assemble integrity.
Firms like BIO INX and Readily3D have developed prepared‑to‑use formulations optimized for volumetric printing, decreasing dealing with variability and enhancing cell viability. These advances spotlight the rising deal with controlling bioink conduct and printer dealing with, stopping cell sedimentation and producing extra constant, biologically viable tissues.
The 3D Printing Trade Awards are again. Make your nominations now.
Do you use a 3D printing start-up? Attain readers, potential traders, and prospects with the 3D Printing Trade Begin-up of Yr competitors.
To remain updated with the most recent 3D printing information, don’t neglect to subscribe to the 3D Printing Trade e-newsletter or comply with us on Linkedin.
Featured picture reveals MagMix, a magnetically actuated mixer. Picture through MIT.

