When company information is uncovered on a devoted leak web site, the implications linger lengthy after the assault fades from the information cycle
12 Feb 2026
•
,
6 min. learn

Within the realm of cybercrime, change is arguably the one fixed. Whereas cyber-extortion as a broader class of crime has proved its endurance, ransomware – its arguably most damaging ‘taste’ – doesn’t dwell or die on encryption alone. The playbook of ‘yore’ largely concerned locking recordsdata or programs and demanding cost for a decryption key, however in recent times campaigns switched to combining encryption with information exfiltration and threats to publish the stolen data.
That is the place devoted leak websites, or information leak websites (DLSs), are available in. First showing in late 2019, DLSs have since change into the spine of the double extortion technique. Menace actors steal company information (earlier than encrypting it) after which weaponize the loot publicly, successfully turning a safety incident right into a full-blown public disaster.
Safety specialists and regulation enforcement have, in fact, been monitoring this shift for years. The FBI and CISA now routinely describe ransomware as a “information theft and extortion” drawback. Public monitoring initiatives similar to Ransomware.dwell level in the identical route, even when exact sufferer counts needs to be handled with warning. The leak websites mirror solely what criminals select to ‘promote’, not the total universe of incidents.
Let’s study the position of DLSs within the ransomware ecosystem and the implications for sufferer organizations.
How do ransomware teams use information leak websites?
Hosted on the darkish internet and accessible by way of the Tor community, the websites usually publish a pattern of stolen information and threaten victims with full public disclosure except cost is made. Typically the fabric is printed after the sufferer refused to collapse, thus additional turning the screw on them. Details about the victims, the extent of stolen materials and even deadlines that are supposed to really feel inexorable are all a part of the technique.
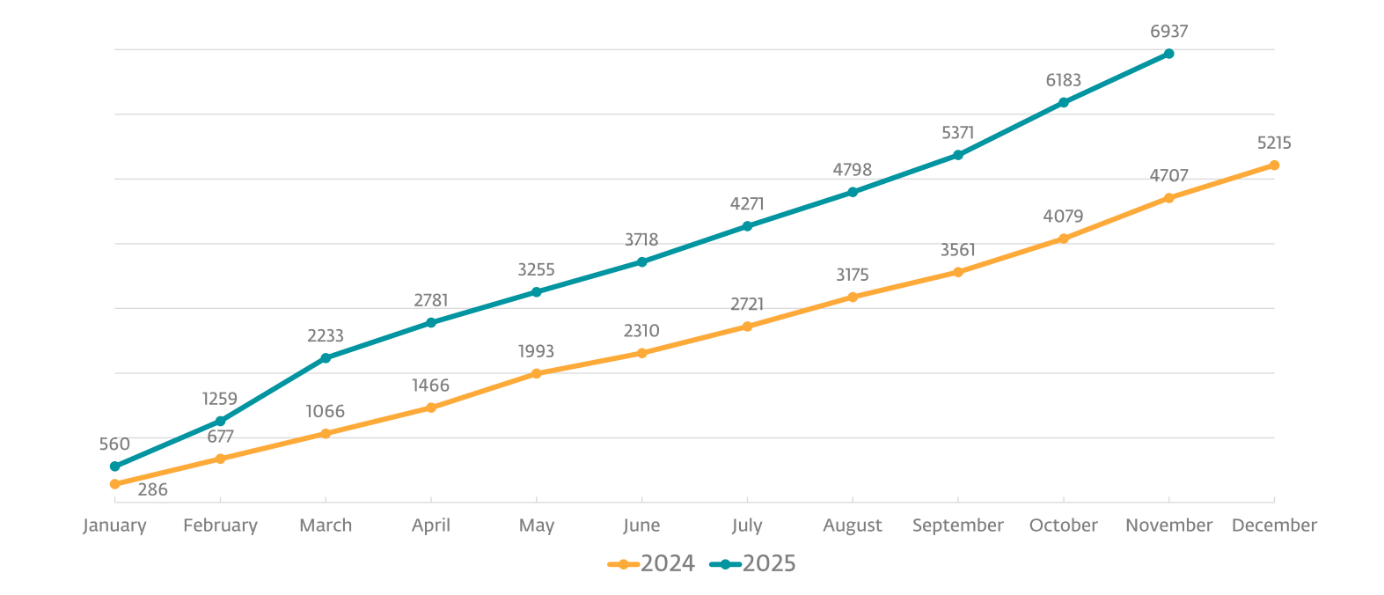
What makes the technique devastating is pace and amplification. As soon as the incident is within the open, a number of dangers are collapsed right into a single, extremely seen second and the sufferer group operates beneath a cloud of suspicion and uncertainty – usually even earlier than its IT and safety employees have a full image of what was stolen or how far the intrusion unfold. And that’s, in fact, the purpose – information leak websites are a coercion software.
That is additionally why they’re rigorously curated. Attackers usually publish simply sufficient materials to indicate that they aren’t bluffing: a handful of contracts or a tranche of emails. Extra is coming except the sufferer caves in.
Certainly, the injury not often stops with the preliminary sufferer. The information, as soon as dumped or resold, turns into gasoline for follow-on crime, and safety groups see it reappear in phishing kits, enterprise electronic mail compromise (BEC) campaigns, and identification fraud schemes. In supply-chain incidents, one breach can ripple outward, exposing the sufferer’s clients and companions. This cascading impact is partly why authorities deal with ransomware as a systemic danger, fairly than a collection of remoted mishaps.
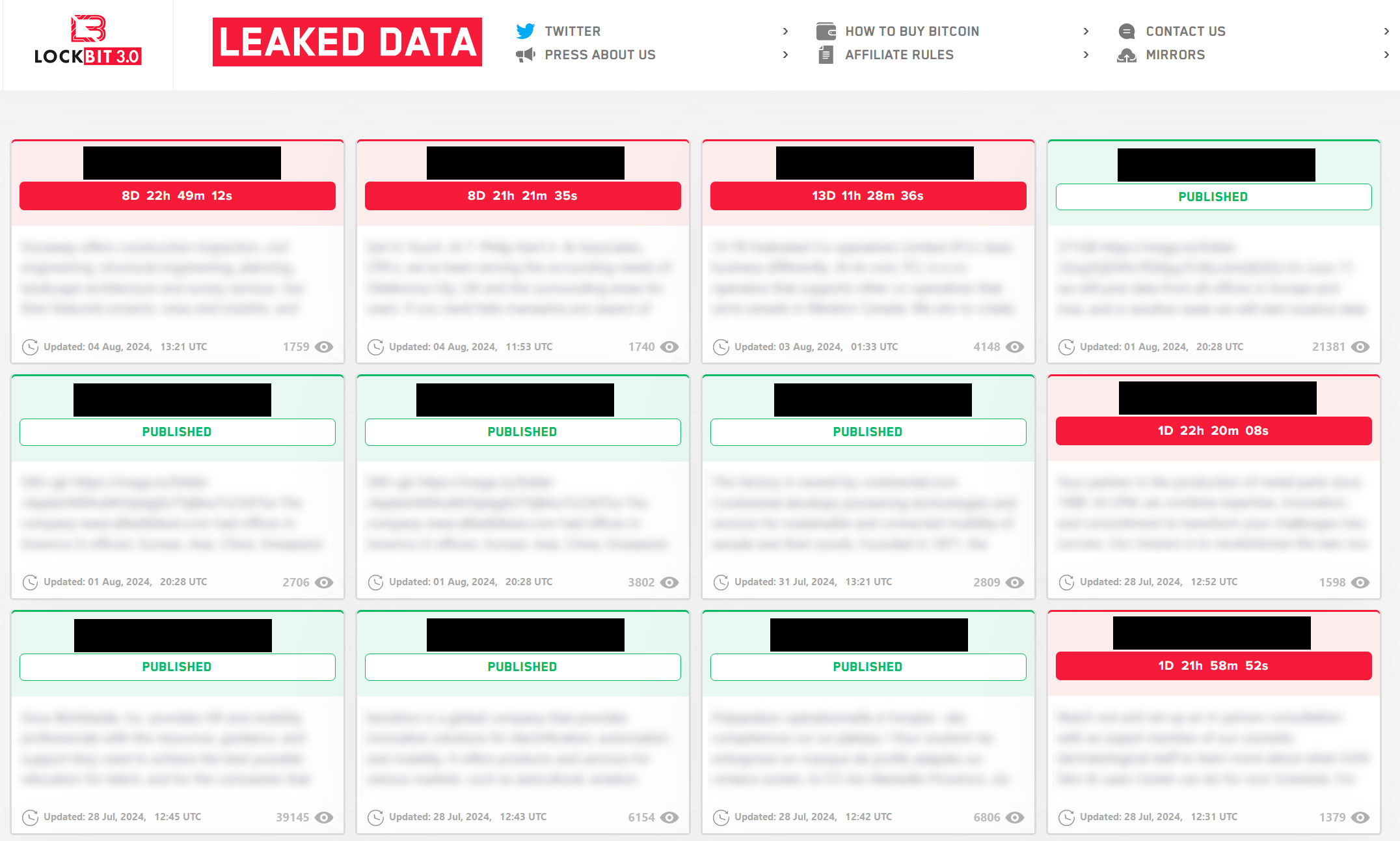
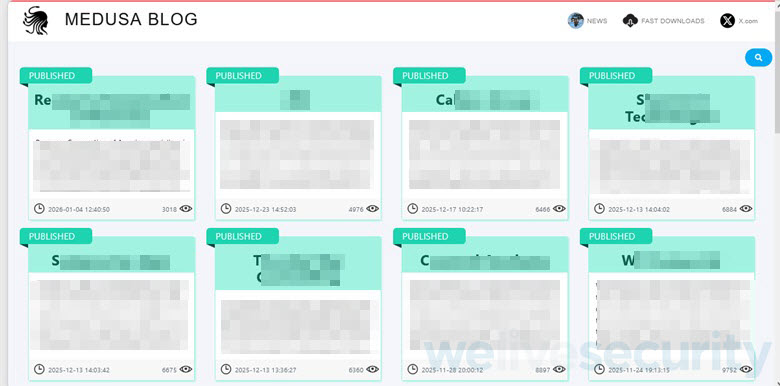
Stress by design
Each factor of a leak web site is designed to maximise psychological strain.
- Proof of unauthorized entry. The gangs publish pattern paperwork, similar to contracts and inside emails, to display that the intrusion was actual and the risk is credible.
- Urgency: Timers and countdowns instill the sensation that point is operating out as selections made beneath time strain usually tend to favor the celebration that controls the clock.
- Public publicity: Even when the stolen information is rarely launched publicly, the mere affiliation with a breach triggers reputational hurt that may take years to restore.
- Regulatory danger: Beneath frameworks like GDPR, HIPAA, and an increasing patchwork of state-level privateness legal guidelines within the US, a confirmed breach involving private information can set off obligatory disclosures, investigations, and fines..
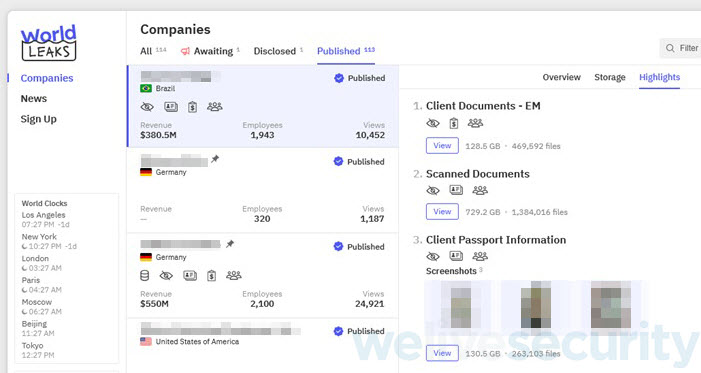
Past extortion
Some ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) operators have expanded what leak websites do. LockBit, earlier than its infrastructure was seized by regulation enforcement in early 2024, ran a bug bounty program on its leak web site, providing funds to anybody who discovered vulnerabilities of their code.
Others publish ‘gigs’ for company insiders, providing cost to workers keen to supply login credentials or weaken safety controls. Nonetheless different websites double as onboarding platforms for the following wave of attackers as attackers promote ‘affiliate packages’, explaining the income break up and easy methods to apply.

Zooming out
Information leak websites work as a result of they hit firms’ weak spots that transcend expertise. A possible information leak triggers a number of dangers without delay: reputational injury, misplaced belief amongst clients and companions, monetary hits, regulatory sanctions, and litigation.
As ransomware gangs additionally promote the stolen data, they feed markets for stolen information and allow follow-on assaults. Some teams have even been noticed skipping encryption completely and as an alternative ‘solely’ seize information and threaten to publish it.
The victims, in the meantime, need to make selections with out sufficient time to consider the implications. The individuals whose private data is caught up within the incident face an extended tail of cleanup, attainable account takeovers and identification fraud.
In opposition to that backdrop, paying up would possibly appear like the (comparatively) simple method out or the least unhealthy possibility. It’s neither. Fee doesn’t assure file or system restoration, nor does it assure that the information stays non-public. Many organizations that paid up had been hit once more inside months. And each cost helps fund the following assault.
For organizations, the ransomware risk calls for complete defensive measures, which embrace:
- Deploying superior safety options with EDR/XDR/MDR capabilities. Amongst different issues, they monitor anomalous habits, similar to unauthorized course of execution and suspicious lateral motion, to cease the risk in its tracks. Certainly, the merchandise are a thorn in criminals‘ sides, who more and more deploy EDR killers in an try and terminate or crash safety merchandise, usually by abusing susceptible drivers.
- Proscribing lateral motion by way of well-defined, stringent entry controls. Zero-Belief ideas improve an organization’s safety posture by eliminating default belief assumptions for any entity. Menace actors usually exploit compromised login credentials and distant desktop protocol entry to manually navigate networks.
- Maintain all of your software program up-to-date. Recognized vulnerabilities are one of many main entry vectors for ransomware actors.
- Sustaining backups saved in remoted, air-gapped environments that ransomware can’t entry or modify. Ransomware’s main goal is to find and encrypt delicate information. Worse, even when victims pay ransoms, flawed decryption processes can lead to everlasting information loss, to not point out different attainable ramifications of paying the ransom. Resilient backups and ransomware remediation capabilities go a great distance in the direction of mitigating injury from the risk.
- Human vigilance, additional refined by well-designed safety consciousness coaching, additionally represents a extremely efficient defensive barrier. An worker who can spot a malicious electronic mail early on removes considered one of ransomware actors’ favourite entry factors, and that alone can markedly lower the danger of an assault victimizing your whole group.
The ransomware evolution continues unabated because the ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) mannequin continues to draw a large felony consumer base and grants quite a few threats longevity and adaptableness. So long as criminals can reliably flip stolen information right into a public spectacle, they may maintain doing it and ransomware will stay a cash machine.

