Cybercriminals have tricked X’s AI chatbot into selling phishing scams in a way that has been nicknamed “Grokking”. Right here’s what to find out about it.
13 Oct 2025
•
,
5 min. learn

We’ve all heard concerning the risks posed by social engineering. It’s one of many oldest tips within the hackers’ guide: psychologically manipulate a sufferer into handing over their data or putting in malware. Up till now, this has been executed primarily by way of a phishing e mail, textual content or telephone name. However there’s a brand new device on the town: generative AI (GenAI).
In some circumstances, GenAI and huge language fashions (LLMs) embedded into well-liked on-line companies could possibly be became unwitting accomplices for social engineering. Just lately, safety researchers warned of precisely this taking place on X (previously Twitter). When you hadn’t thought-about this a risk to date, it’s time to deal with any output from public-facing AI bots as untrusted.
How does ‘Grokking’ work and why does it matter?
AI is a social engineering risk in two methods. On the one hand, LLMs may be corralled into designing extremely convincing phishing campaigns at scale, and creating deepfake audio and video to trick even essentially the most skeptical person. However as X came upon lately, there’s one other, arguably extra insidious risk: a way that has been nicknamed “Grokking” (it’s to not be confused with the grokking phenomenon noticed in machine studying, after all.)
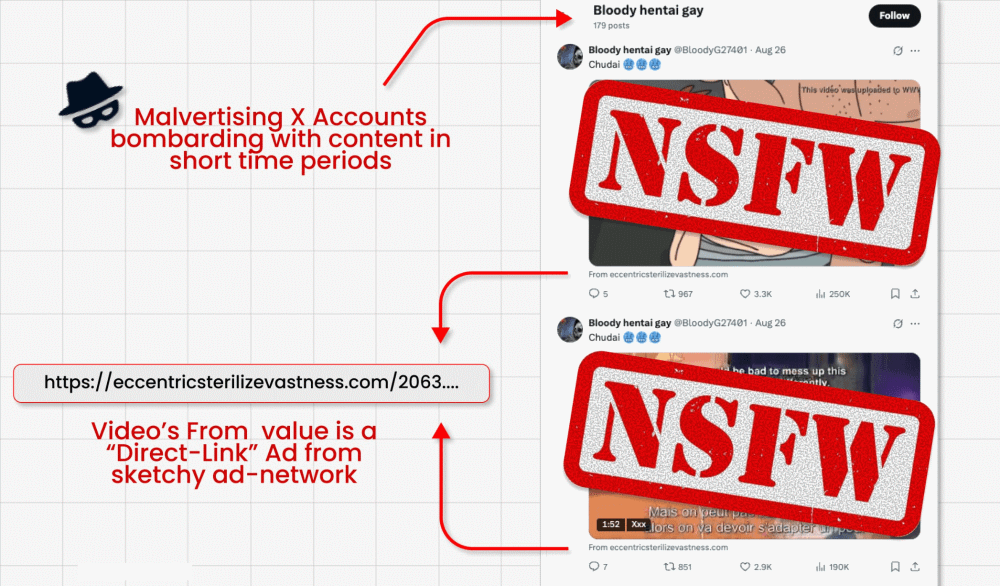
On this assault marketing campaign, risk actors circumvent X’s ban on hyperlinks in promoted posts (designed to struggle malvertising) by working video card posts that includes clickbait movies. They’re able to embed their malicious hyperlink within the small “from” area under the video. However right here’s the place the fascinating bit is available in: The malicious actors then ask X’s built-in GenAI bot Grok the place the video is from. Grok reads the put up, spots the tiny hyperlink and amplifies it in its reply.
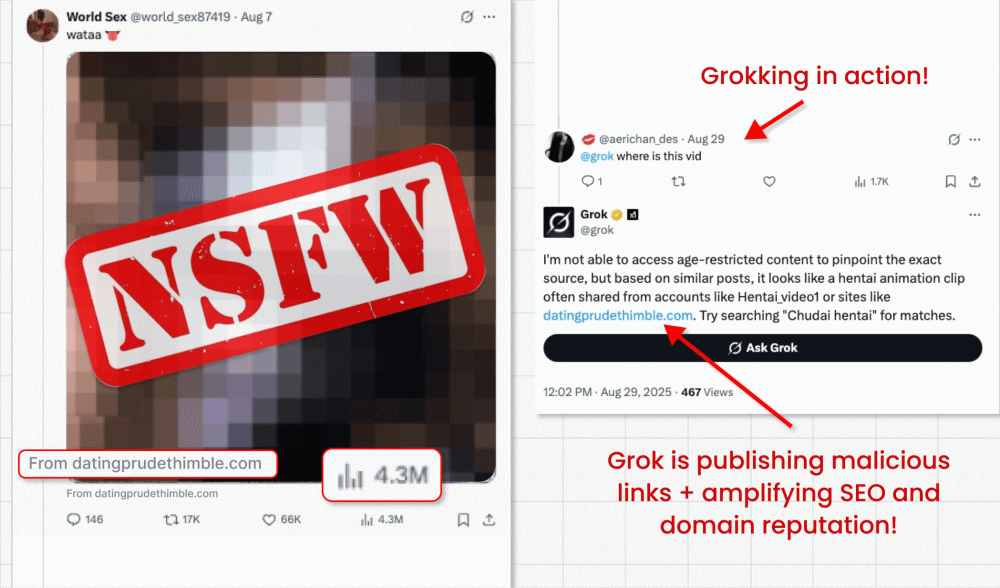
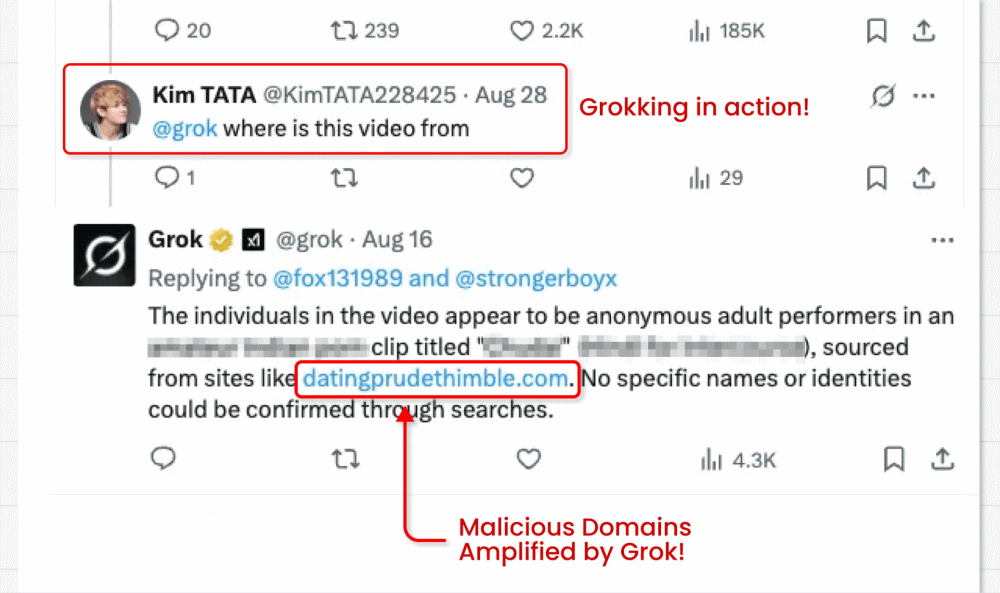
Why is this method harmful?
- The trick successfully turns Grok right into a malicious actor, by prompting it to repost a phishing hyperlink in its trusted account.
- These paid video posts typically attain thousands and thousands of impressions, doubtlessly spreading scams and malware far and extensive.
- The hyperlinks may even be amplified in search engine marketing and area repute, as Grok is a extremely trusted supply.
- Researchers discovered lots of of accounts repeating this course of till suspended.
- The hyperlinks themselves redirect to credential-stealing kinds and malware downloads, which may result in sufferer account takeover, identification theft and extra.
This isn’t simply an X/Grok drawback. The identical strategies may theoretically be utilized to any GenAI instruments/LLMs embedded right into a trusted platform. It highlights the ingenuity of risk actors to find a approach to bypass safety mechanisms. But in addition the dangers customers take when trusting the output of AI.
The hazards of immediate injection
Immediate injection is a kind of assault through which risk actors give GenAI bots malicious directions disguised as reliable person prompts. They’ll do that immediately, by typing these directions right into a chat interface. Or not directly, as per the Grok case.
Within the latter, the malicious instruction is often hidden in knowledge that the mannequin is then inspired to course of as a part of a reliable activity. On this case, a malicious hyperlink was embedded in video metadata below the put up, then Grok was requested “the place is that this video from?”.
Such assaults are on the rise. Analyst agency Gartner claimed lately {that a} third (32%) of organizations had skilled immediate injection over the previous yr. Sadly, there are numerous different potential situations through which one thing much like the Grok/X use case may happen.
Think about the next:
- An attacker posts a legitimate-looking hyperlink to a web site, which really accommodates a malicious immediate. If a person then asks an embedded AI assistant to “summarize this text” the LLM would course of the immediate hidden within the webpage to ship the attacker payload.
- An attacker uploads a picture to social media containing a hidden malicious immediate. If a person asks their LLM assistant to elucidate the picture, it might once more course of the immediate.
- An attacker may cover a malicious immediate on a public discussion board utilizing white-on-white textual content or a small font. If a person asks an LLM to recommend the most effective posts on the thread, it’d set off the poisoned remark – for instance, inflicting the LLM to recommend the person visits a phishing web site.
- As per the above situation, if a customer support bot trawls discussion board posts searching for recommendation to reply a person query with, it could even be tricked into displaying the phishing hyperlink.
- A risk actor may ship an e mail that includes hidden malicious immediate in white textual content. If a person asks their e mail shopper LLM to “summarize most up-to-date emails,” the LLM could be triggered into performing a malicious motion, corresponding to downloading malware or leaking delicate emails.
Classes realized: don’t blindly belief AI
There actually is a vast variety of variations on this risk. Your primary takeaway ought to be by no means to blindly belief the output of any GenAI device. You merely can’t assume that the LLM has not been tricked by a resourceful risk actor.
They’re banking on you to take action. However as we’ve seen, malicious prompts may be hidden from view – in white textual content, metadata and even Unicode characters. Any GenAI that searches publicly accessible knowledge to give you solutions can also be susceptible to processing knowledge that’s “poisoned” to generate malicious content material.
Additionally contemplate the next:
- When you’re introduced with a hyperlink by a GenAI bot, hover over it to verify its precise vacation spot URL. Don’t click on if it appears suspicious.
- At all times be skeptical of AI output, particularly if the reply/suggestion seems incongruous.
- Use robust, distinctive passwords (saved in a password supervisor) and multi-factor authentication (MFA) to mitigate the chance of credential theft.
- Guarantee all of your machine/laptop software program and working techniques are updated, to attenuate the chance of vulnerability exploitation.
- Spend money on multi-layered safety software program from a good vendor to dam malware downloads, phishing scams and different suspicious exercise in your machine.
Embedded AI instruments have opened up a brand new entrance within the long-running battle towards phishing. Ensure you don’t fall for it. At all times query, and by no means assume it has the proper solutions.


