Russian cybercriminals have laundered over $35 million in stolen cryptocurrency linked to the devastating 2022 LastPass breach, in line with new forensic evaluation by blockchain intelligence agency TRM Labs.
The 2022 assault uncovered encrypted password vaults belonging to roughly 30 million prospects worldwide.
Whereas the vaults have been initially protected by encryption, attackers who downloaded them may crack weaker grasp passwords offline, making a multi-year window to steal belongings.
New waves of theft all through 2024 and 2025 have weaponized these compromised credentials, notably concentrating on customers holding cryptocurrency.
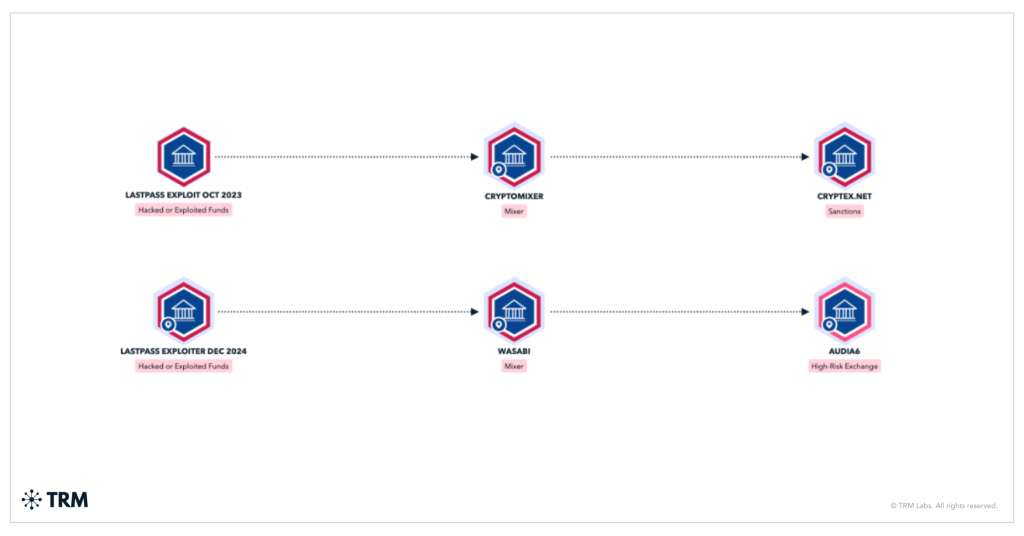
TRM’s analysis traced roughly $28 million in stolen Bitcoin by way of Wasabi Pockets, a cryptocurrency mixer designed to obscure transaction trails, and recognized one other $7 million shifting by way of comparable laundering pathways.
The stolen funds in the end converged at two high-risk Russian exchanges: Cryptex (sanctioned by OFAC in 2024) and Audi6, each traditionally linked to cybercriminal exercise.
“The attackers used a constant operational signature,” TRM researchers defined. Stolen Bitcoin keys have been imported into an identical pockets software program, producing recognizable transaction patterns.
Non-Bitcoin belongings have been quickly transformed to Bitcoin by way of swap companies earlier than being deposited into mixing companies, a way that, in principle, ought to obscure criminals’ identities.
But TRM’s proprietary “demixing” methods revealed what mixers can not cover: behavioral fingerprints that linked exercise earlier than and after mixing to the identical actors.
Regardless of CoinJoin obfuscation, researchers recognized clustering patterns, withdrawal timing, and pockets interactions that pointed to coordinated Russian cybercrime infrastructure.
The findings underscore two crucial insights. First, mixing companies have gotten much less dependable as risk actors preserve constant infrastructure over time.
Second, Russian exchanges proceed functioning as systemic enablers of international cybercrime, facilitating hundreds of thousands in illicit fund transfers regardless of worldwide enforcement stress.
Early Wasabi withdrawals occurred inside days of pockets drains, suggesting that attackers themselves orchestrated the laundering relatively than reselling stolen keys to different criminals.
This operational continuity strengthens confidence in attribution of the unique 2022 intrusion to Russian-based actors. Nonetheless, definitive attribution of the unique 2022 intrusion stays unconfirmed.
The LastPass case demonstrates how single credential breaches cascade throughout years, and the way cybercriminal ecosystems exploit geographic monetary infrastructure to monetize stolen information at scale.
For the 25 million affected customers, the risk stays energetic a stark reminder that breached credentials signify persistent, long-tail danger.
Observe us on Google Information, LinkedIn, and X to Get Instantaneous Updates and Set GBH as a Most well-liked Supply in Google.

