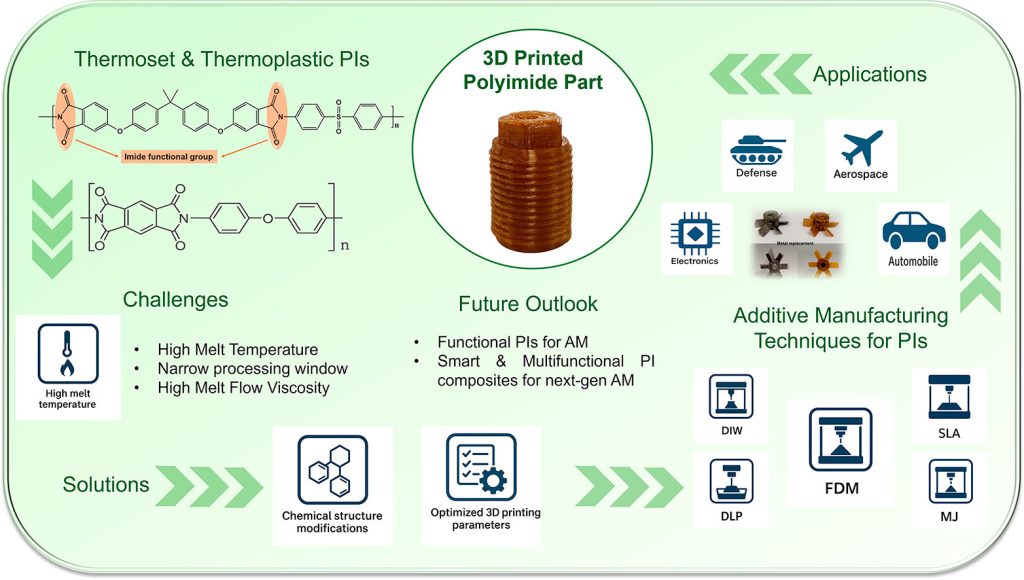
A complete evaluation printed on ScienceDirect by researchers from the RMIT Centre for Additive Manufacturing in Melbourne and India’s CSIR-Nationwide Chemical Laboratory (CSIR-NCL) outlines present progress in additive manufacturing (AM) of polyimides (PIs). The examine, co-authored with the Academy of Scientific and Progressive Analysis (AcSIR) in Ghaziabad, examines how polymer chemistry and processing methods are enabling the 3D printing of high-performance PIs beforehand thought-about unprocessable resulting from insolubility, infusibility, and slim temperature ranges.
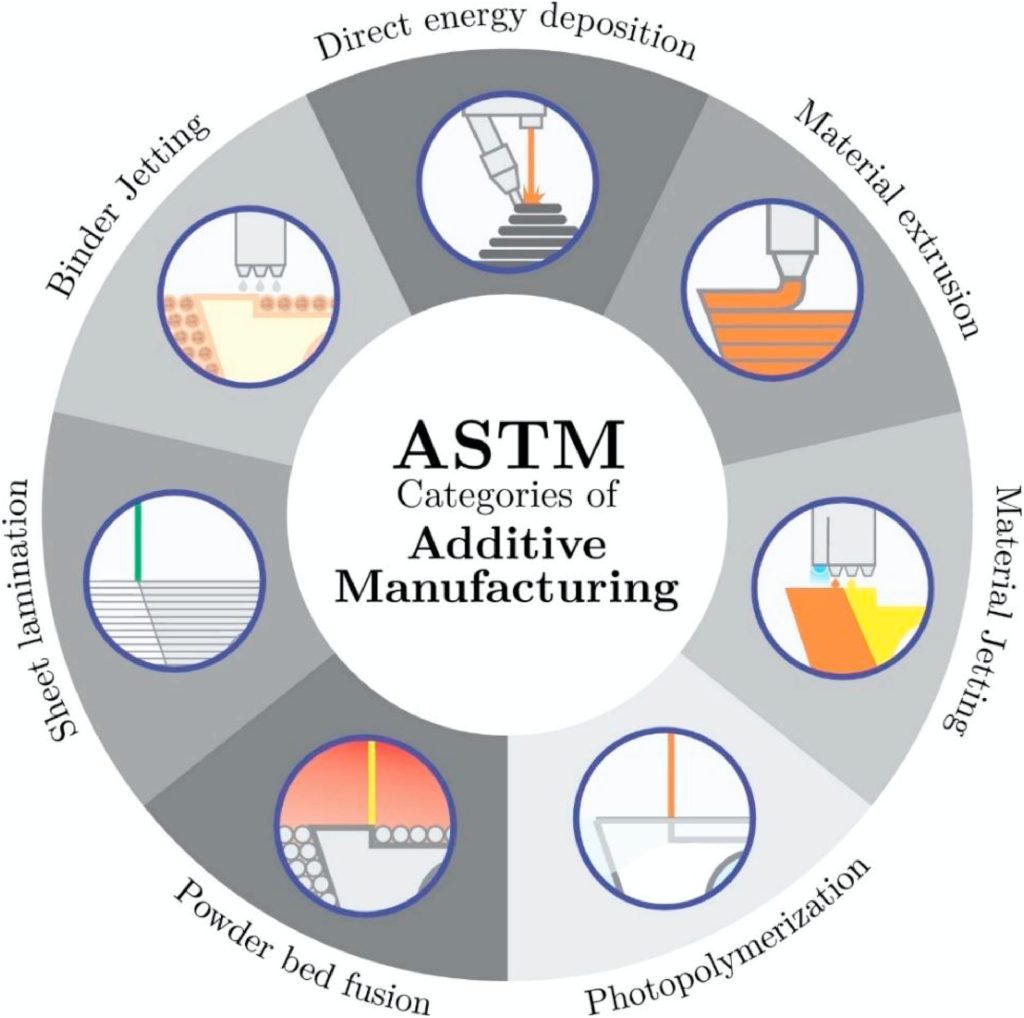
Polyimides are valued for his or her thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical energy, however their processing stays difficult. Standard fabrication depends on soluble poly(amic acid) precursors which might be later imidized at excessive temperatures, whereas thermoplastic PIs (TPIs) demand exact management of viscosity and thermal home windows. The evaluation identifies vat photopolymerization (VPP), materials extrusion (MEX), direct ink writing (DIW), and materials jetting (MJ) as the primary AM pathways used to adapt PIs for complicated buildings, high-temperature elements, and multifunctional gadgets.
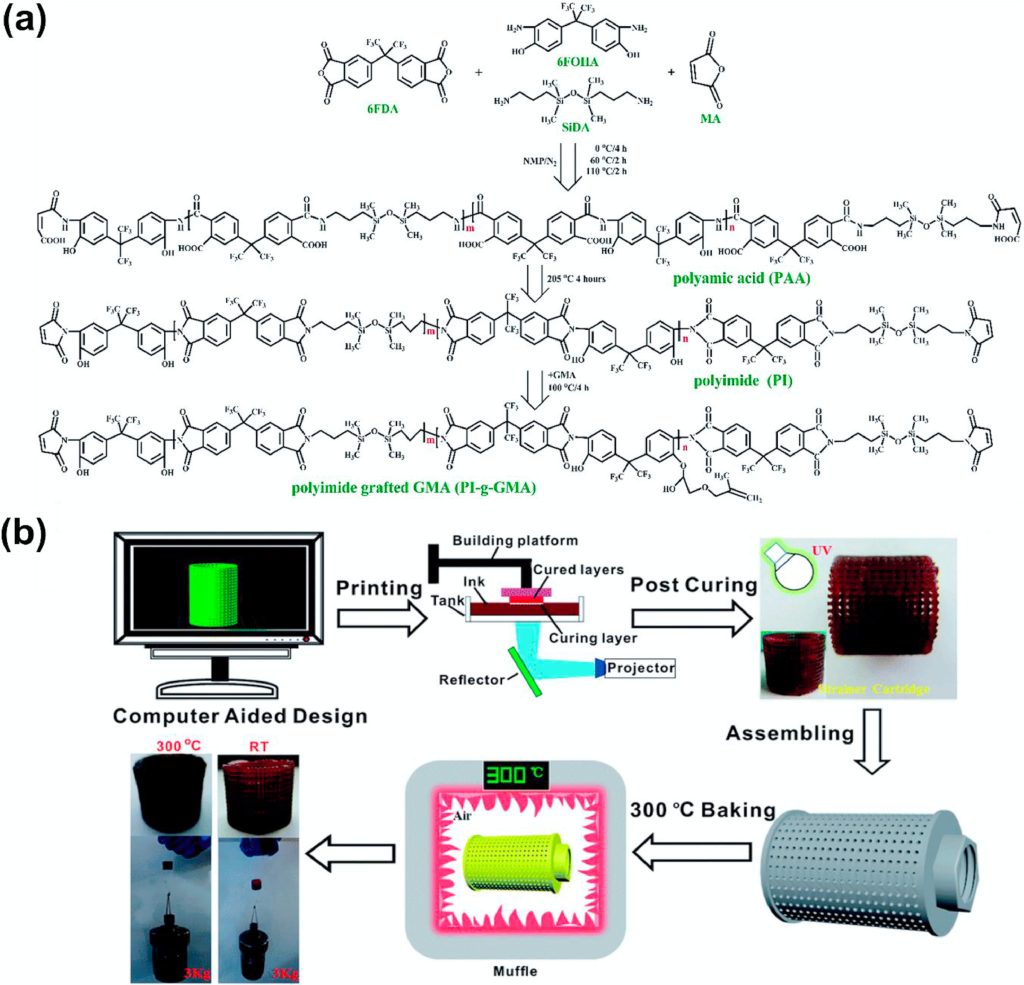
VPP was the primary AM route demonstrated for polyimides. Two unbiased research printed on March 3, 2017, reported the 3D printing of PIs utilizing digital mild processing (DLP) and mask-projection stereolithography (MPSL). Guo et al. developed a solvent-free, photocurable polyimide oligomer synthesized from 6FDA and 6FOHA monomers with glycidyl methacrylate modification. The ensuing methacrylate-functionalized resin enabled ultraviolet curing and high-resolution printing with out solvent elimination. Printed micro-oil filters exhibited sturdy mechanical and thermal properties appropriate for high-temperature purposes.
In parallel, one other examine achieved the primary MPSL printing of PMDA-ODA polyimide, commercially often called Kapton™, utilizing poly(amic ester) precursors with pendant acrylate teams. After printing, solvent elimination and thermal imidization at 350 °C yielded absolutely imidized buildings with 52 % isotropic shrinkage. Subsequent work by Arrington et al. pyrolyzed the identical organogel buildings at 1000 °C to type dense, monolithic carbon elements that retained their geometry with roughly 55 % linear shrinkage. Additional developments embody photocurable PI/PTFE composites for self-lubricating bearings, shape-memory PI inks for 4D printing, and hybrid VPP–DIW processes for high-viscosity resins.

Materials extrusion utilizing thermoplastic polyimides
Extrusion-based 3D printing, together with fused filament fabrication (FFF) and direct ink extrusion, has targeted totally on thermoplastic PIs akin to ULTEM™ 9085, ULTEM™ 1010, and EXTEM™ VH1003. These polyetherimide and polyimide blends mix processability with thermal energy appropriate for aerospace elements. Research summarized within the evaluation present that construct orientation strongly influences mechanical efficiency. Specimens printed within the ZX orientation exhibit decreased tensile and flexural energy resulting from weak interlayer bonding, whereas horizontally printed elements present larger compressive energy. Optimum nozzle temperatures between 320 °C and 340 °C stability interlayer adhesion and viscosity; overheating causes foaming and delamination, whereas decrease temperatures lead to incomplete move.
Steady fiber reinforcement additional improves efficiency. Ye et al. demonstrated separated steady carbon-fiber bolstered TPI composites with tensile and bending energy will increase of 214 % and 167 % in comparison with pure TPI. Further analysis optimized nozzle diameter, drying time, and cooling situations to cut back porosity and enhance bonding. ULTEM-based research examined the affect of raster sample, infill density, and post-printing annealing on energy and fatigue life. Fiber-reinforced variants akin to carbon-fiber-wrapped ULTEM™ 9085 and CF-filled ULTEM™ 1010 confirmed improved stiffness, whereas temperature publicity and environmental ageing affected sturdiness. Collectively, these findings set up parameter home windows for printing high-temperature engineering polymers with reproducible mechanical properties.

Direct ink writing and UV-assisted curing
DIW has change into a versatile platform for processing polyimide pastes and precursor inks. Utilizing shear-thinning formulations, DIW permits complicated geometries whereas preserving dimensional accuracy after curing. PI/silica composite aerogels printed by way of DIW and thermally imidized present thermal stability between −50 °C and 1300 °C, low thermal conductivity, and excessive flame resistance. Solvent-free photocurable comb poly(amic acid) inks containing glycidyl methacrylate teams obtain lower than 6 % shrinkage and glass-transition temperatures round 204 °C.
Aqueous PAA salt hydrogels present an environmentally safer route for DIW by enabling sol-gel transitions in water. UV-assisted DIW (UV-DIW) utilizing hydroxyethyl methacrylate-modified PAA precursors produces polyimide buildings with excessive modulus and low shrinkage after staged imidization. Further research developed gradient conductive MXene/CNT/PI aerogels for electromagnetic interference shielding with efficiencies as much as 68 dB and freeze-casting assisted DIW for honeycomb PI aerogels with sound absorption coefficients peaking at 0.86. Different DIW work contains tribology-enhanced PI/MoS₂ composites, thermosetting SiO₂-filled PIs for aerospace buildings, and solvent-free polyamide-imide scaffolds for high-temperature elements.


Materials jetting and composite reinforcement
Materials jetting has been explored by way of bismaleimide (BMI) precursors and multijet fusion (MJF) of PI-fiber composites. BMI oligomers with molecular weights between 689 and 5000 g/mol polymerize through photo-induced cyclodimerization, permitting fast UV curing into crosslinked thermoset PIs with excessive warmth resistance. MJF research incorporating brief chopped PI fibers right into a PA12 matrix demonstrated 43 % larger tensile energy and 46 % larger flexural energy in comparison with neat PA12. Thermogravimetric and differential scanning calorimetry evaluation confirmed enhanced decomposition temperature and crystallinity. Fiber alignment alongside the print path created anisotropic reinforcement, whereas annealing improved energy however elevated brittleness resulting from larger crystallinity. Fiber contents exceeding 10 wt % decreased printability by introducing porosity.
The RMIT and CSIR-NCL authors establish remaining obstacles to scalable AM of polyimides. Excessive processing temperatures above 350 °C demand specialised {hardware}, whereas elevated soften viscosity limits move in extrusion techniques. Hygroscopic conduct requires managed drying to stop voids, and post-processing imidization introduces shrinkage and inside stress. Rheological optimization, improved mattress adhesion, and temperature-controlled chambers are advisable to mitigate warping. Sustainability is one other concern: the examine highlights the necessity for recyclable TPI techniques and solvent-free or deconstructable chemistries that preserve efficiency with out compromising stability.

In keeping with the evaluation, future analysis will concentrate on molecular tailoring for functionalization, 4D printing of shape-memory PIs, and integration of PIs with metals or ceramics for hybrid buildings. AI-driven supplies design and course of optimization are additionally anticipated to speed up formulation discovery. The authors conclude that combining chemical design with high-temperature printer know-how might place polyimides as viable options to metals in aerospace, electronics, and vitality purposes, remodeling high-performance polymer manufacturing by way of additive strategies.
Assist form the 2025 3D Printing Trade Awards. Join the 3DPI Professional Committee right now.
Are you constructing the following huge factor in 3D printing? Be part of the 3D Printing Trade Begin-up of the Yr competitors and broaden your attain.
Subscribe to the 3D Printing Trade publication to remain up to date with the most recent information and insights.
Featured picture exhibits (a) Synthesis of photosensitive PI oligomer PI-g-GMA and (b) step-by-step process for DLP 3D printing of PI ink. Picture through Royal Society of Chemistry.

