The dexterity hole: from human hand to robotic hand
Observe your personal hand. As you learn this, it’s holding your telephone or clicking your mouse with seemingly easy grace. With over 20 levels of freedom, human palms possess extraordinary dexterity, which may grip a heavy hammer, rotate a screwdriver, or immediately regulate when one thing slips.
With an identical construction to human palms, dexterous robotic palms provide nice potential:
Common adaptability: Dealing with varied objects from delicate needles to basketballs, adapting to every distinctive problem in actual time.
Fantastic manipulation: Executing complicated duties like key rotation, scissor use, and surgical procedures which can be unattainable with easy grippers.
Talent switch: Their similarity to human palms makes them ultimate for studying from huge human demonstration knowledge.
Regardless of this potential, most present robots nonetheless depend on easy “grippers” as a result of difficulties of dexterous manipulation. The pliers-like grippers are succesful solely of repetitive duties in structured environments. This “dexterity hole” severely limits robots’ position in our every day lives.
Amongst all manipulation expertise, greedy stands as probably the most elementary. It’s the gateway by means of which many different capabilities emerge. With out dependable greedy, robots can not decide up instruments, manipulate objects, or carry out complicated duties. Subsequently, we deal with equipping dexterous robots with the potential to robustly grasp various objects on this work.
The problem: why dexterous greedy stays elusive
Whereas people can grasp nearly any object with minimal acutely aware effort, the trail to dexterous robotic greedy is fraught with elementary challenges which have stymied researchers for many years:
Excessive-dimensional management complexity. With 20+ levels of freedom, dexterous palms current an astronomically massive management area. Every finger’s motion impacts your complete grasp, making it extraordinarily tough to find out optimum finger trajectories and drive distributions in real-time. Which finger ought to transfer? How a lot drive needs to be utilized? The right way to regulate in real-time? These seemingly easy questions reveal the extraordinary complexity of dexterous greedy.
Generalization throughout various object shapes. Totally different objects demand basically completely different grasp methods. For instance, spherical objects require enveloping grasps, whereas elongated objects want precision grips. The system should generalize throughout this huge variety of shapes, sizes, and supplies with out express programming for every class.
Form uncertainty beneath monocular imaginative and prescient. For sensible deployment in every day life, robots should depend on single-camera methods—probably the most accessible and cost-effective sensing answer. Moreover, we can not assume prior data of object meshes, CAD fashions, or detailed 3D info. This creates elementary uncertainty: depth ambiguity, partial occlusions, and perspective distortions make it difficult to precisely understand object geometry and plan applicable grasps.
Our strategy: RobustDexGrasp
To handle these elementary challenges, we current RobustDexGrasp, a novel framework that tackles every problem with focused options:
Instructor-student curriculum for high-dimensional management. We skilled our system by means of a two-stage reinforcement studying course of: first, a “instructor” coverage learns ultimate greedy methods with privileged info (full object form and tactile sensors) by means of in depth exploration in simulation. Then, a “scholar” coverage learns from the instructor utilizing solely real-world notion (single-view level cloud, noisy joint positions) and adapts to real-world disturbances.
Hand-centric “instinct” for form generalization. As an alternative of capturing full 3D form options, our technique creates a easy “psychological map” that solely solutions one query: “The place are the surfaces relative to my fingers proper now?” This intuitive strategy ignores irrelevant particulars (like shade or ornamental patterns) and focuses solely on what issues for the grasp. It’s the distinction between memorizing each element of a chair versus simply realizing the place to place your palms to raise it—one is environment friendly and adaptable, the opposite is unnecessarily difficult.
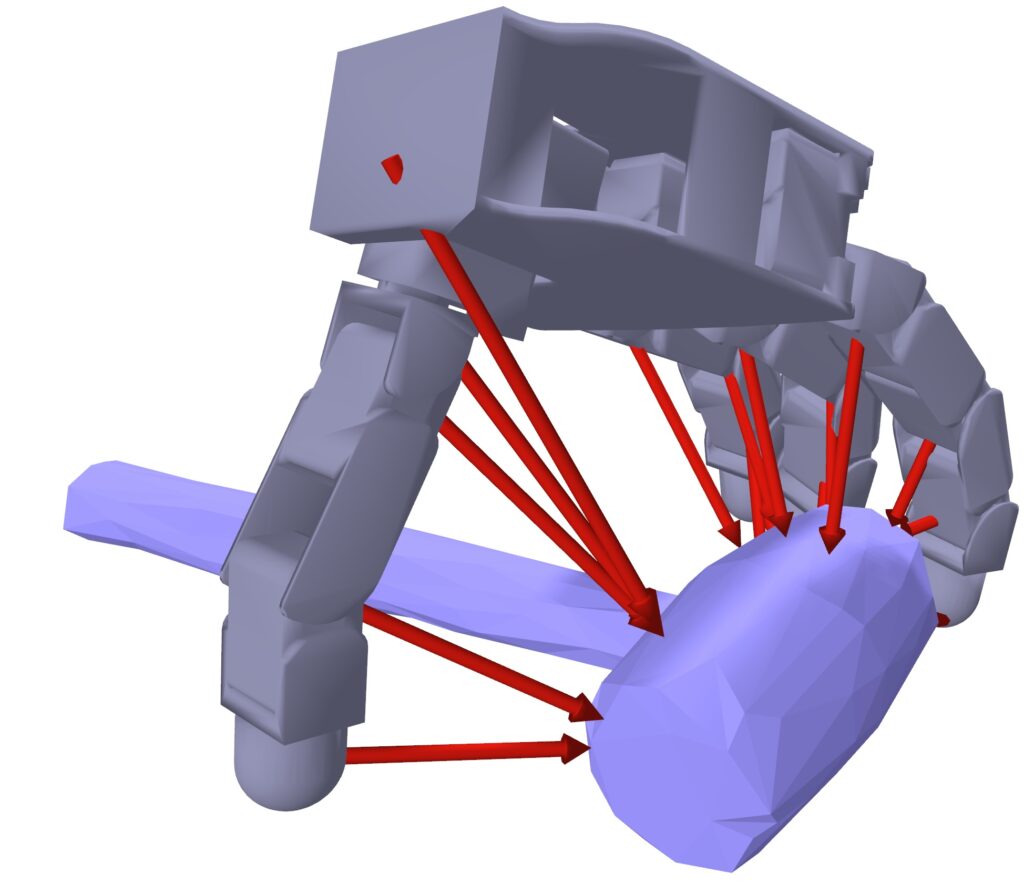
Multi-modal notion for uncertainty discount. As an alternative of counting on imaginative and prescient alone, we mix the digicam’s view with the hand’s “physique consciousness” (proprioception—realizing the place its joints are) and reconstructed “contact sensation” to cross-check and confirm what it’s seeing. It’s like the way you would possibly squint at one thing unclear, then attain out to the touch it to make certain. This multi-sense strategy permits the robotic to deal with difficult objects that will confuse vision-only methods—greedy a clear glass turns into potential as a result of the hand “is aware of” it’s there, even when the digicam struggles to see it clearly.
The outcomes: from laboratory to actuality
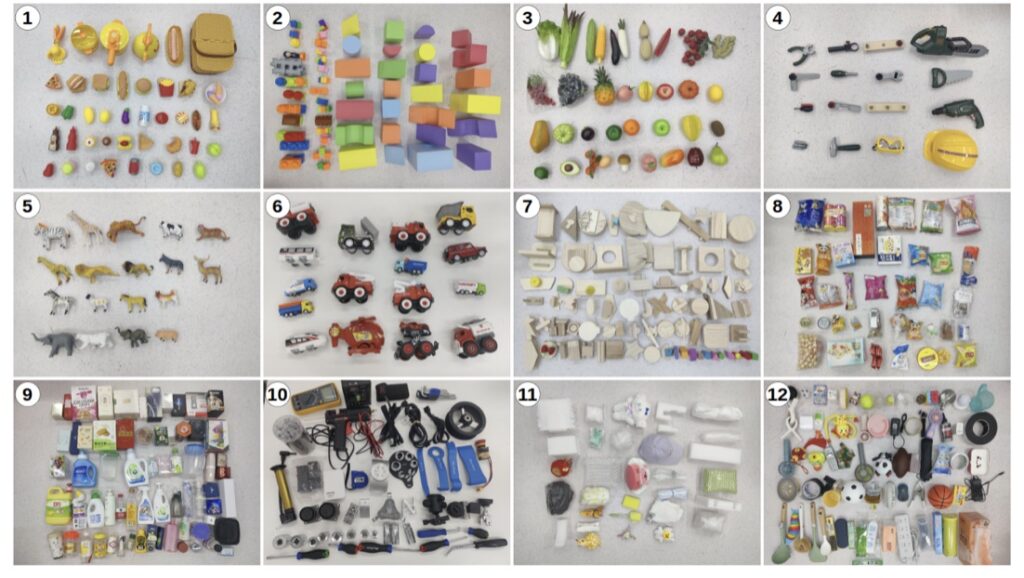

Skilled on simply 35 simulated objects, our system demonstrates glorious real-world capabilities:
Generalization: It achieved a 94.6% success price throughout a various take a look at set of 512 real-world objects, together with difficult objects like skinny containers, heavy instruments, clear bottles, and comfortable toys.
Robustness: The robotic may keep a safe grip even when a big exterior drive (equal to a 250g weight) was utilized to the grasped object, exhibiting far higher resilience than earlier state-of-the-art strategies.
Adaptation: When objects have been unintentionally bumped or slipped from its grasp, the coverage dynamically adjusted finger positions and forces in real-time to recuperate, showcasing a degree of closed-loop management beforehand tough to attain.
Past choosing issues up: enabling a brand new period of robotic manipulation
RobustDexGrasp represents a vital step towards closing the dexterity hole between people and robots. By enabling robots to know practically any object with human-like reliability, we’re unlocking new potentialities for robotic purposes past greedy itself. We demonstrated how it may be seamlessly built-in with different AI modules to carry out complicated, long-horizon manipulation duties:
Greedy in muddle: Utilizing an object segmentation mannequin to establish the goal object, our technique permits the hand to choose a selected merchandise from a crowded pile regardless of interference from different objects.
Process-oriented greedy: With a imaginative and prescient language mannequin because the high-level planner and our technique offering the low-level greedy talent, the robotic hand can execute grasps for particular duties, reminiscent of cleansing up the desk or taking part in chess with a human.
Dynamic interplay: Utilizing an object monitoring module, our technique can efficiently management the robotic hand to know objects transferring on a conveyor belt.
Trying forward, we purpose to beat present limitations, reminiscent of dealing with very small objects (which requires a smaller, extra anthropomorphic hand) and performing non-prehensile interactions like pushing. The journey to true robotic dexterity is ongoing, and we’re excited to be a part of it.
Learn the work in full

Hui Zhang
is a PhD candidate at ETH Zurich.

