By Kristýna Janovská and Pavel Surynek
Think about if all of our automobiles may drive themselves – autonomous driving is changing into potential, however to what extent? To get a car someplace by itself could not appear so tough if the route is evident and effectively outlined, however what if there are extra automobiles, every making an attempt to get to a special place? And what if we add pedestrians, animals and different unaccounted for parts? This downside has not too long ago been more and more studied, and already utilized in situations corresponding to warehouse logistics, the place a bunch of robots transfer containers in a warehouse, every with its personal purpose, however all shifting whereas ensuring to not collide and making their routes – paths – as quick as potential. However the best way to formalize such an issue? The reply is MAPF – multi-agent path discovering [Silver, 2005].
Multi-agent path discovering describes an issue the place we’ve a bunch of brokers – robots, autos and even individuals – who’re every making an attempt to get from their beginning positions to their purpose positions with out ever colliding (being in the identical place on the similar time).
Usually, this downside has been solved on graphs. Graphs are constructions which are in a position to simplify an surroundings utilizing its focal factors and interconnections between them. These factors are known as vertices and might symbolize, for instance, coordinates. They’re related by edges, which join neighbouring vertices and symbolize distances between them.
If nevertheless we are attempting to resolve a real-life state of affairs, we attempt to get as near simulating actuality as potential. Due to this fact, discrete illustration (utilizing a finite variety of vertices) could not suffice. However the best way to search an surroundings that’s steady, that’s, one the place there’s principally an infinite quantity of vertices related by edges of infinitely small sizes?
That is the place one thing known as sampling-based algorithms comes into play. Algorithms corresponding to RRT* [Karaman and Frazzoli, 2011], which we utilized in our work, randomly choose (pattern) coordinates in our coordinate area and use them as vertices. The extra factors which are sampled, the extra correct the illustration of the surroundings is. These vertices are related to that of their nearest neighbours which minimizes the size of the trail from the place to begin to the newly sampled level. The trail is a sequence of vertices, measured as a sum of the lengths of edges between them.
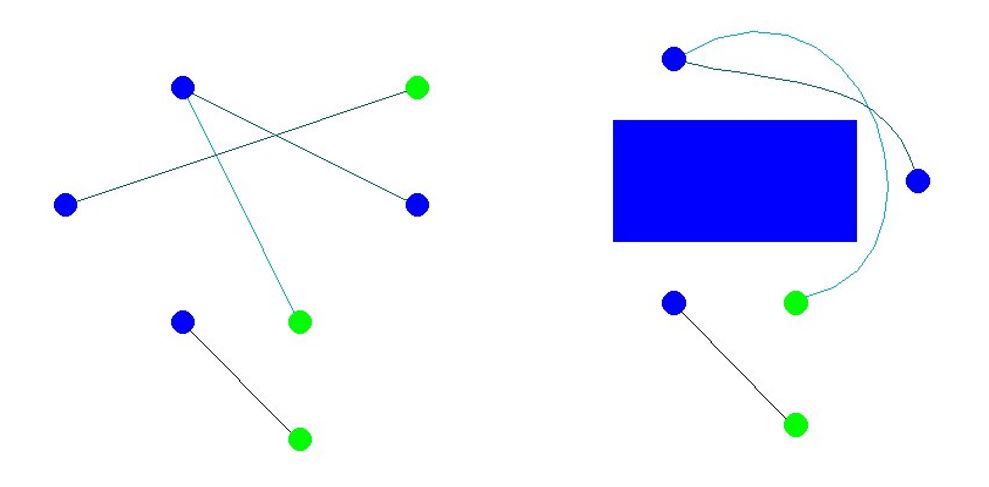 Determine 1: Two examples of paths connecting beginning positions (blue) and purpose positions (inexperienced) of three brokers. As soon as an impediment is current, brokers plan easy curved paths round it, efficiently avoiding each the impediment and one another.
Determine 1: Two examples of paths connecting beginning positions (blue) and purpose positions (inexperienced) of three brokers. As soon as an impediment is current, brokers plan easy curved paths round it, efficiently avoiding each the impediment and one another.
We are able to get a near optimum path this manner, although there’s nonetheless one downside. Paths created this manner are nonetheless considerably bumpy, because the transition between completely different segments of a path is sharp. If a car was to take this path, it will most likely have to show itself directly when it reaches the top of a phase, as some robotic vacuum cleaners do when shifting round. This slows the car or a robotic down considerably. A means we will remedy that is to take these paths and easy them, in order that the transitions are now not sharp, however easy curves. This manner, robots or autos shifting on them can easily journey with out ever stopping or slowing down considerably when in want of a flip.
Our paper [Janovská and Surynek, 2024] proposed a way for multi-agent path discovering in steady environments, the place brokers transfer on units of easy paths with out colliding. Our algorithm is impressed by the Battle Based mostly Search (CBS) [Sharon et al., 2014]. Our extension right into a steady area known as Steady-Atmosphere Battle-Based mostly Search (CE-CBS) works on two ranges:
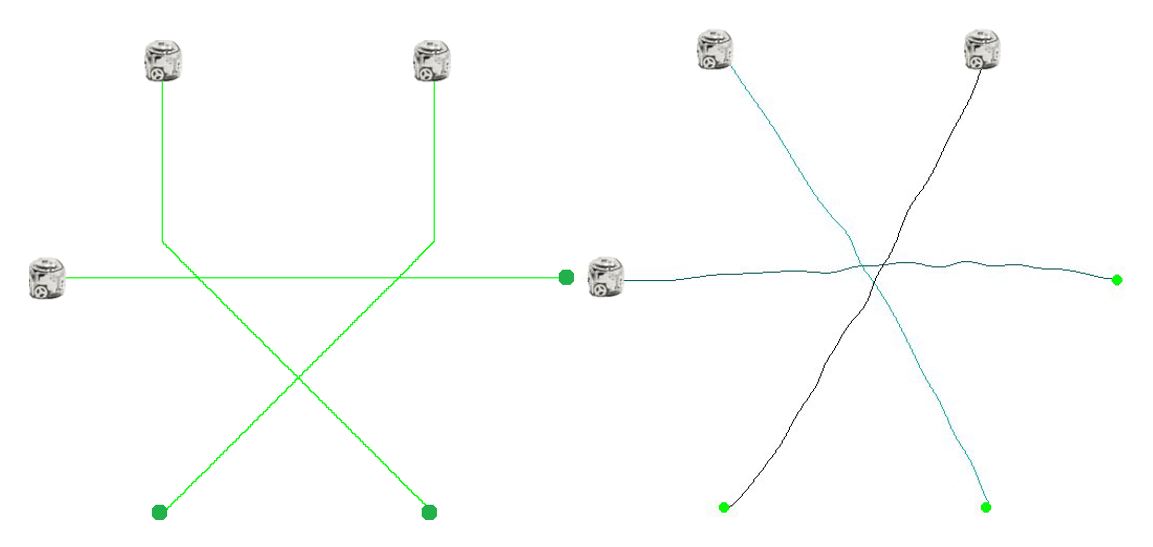 Determine 2: Comparability of paths discovered with discrete CBS algorithm on a 2D grid (left) and CE-CBS paths in a steady model of the identical surroundings. Three brokers transfer from blue beginning factors to inexperienced purpose factors. These experiments are carried out within the Robotic Brokers Laboratory at School of Data Know-how of the Czech Technical College in Prague.
Determine 2: Comparability of paths discovered with discrete CBS algorithm on a 2D grid (left) and CE-CBS paths in a steady model of the identical surroundings. Three brokers transfer from blue beginning factors to inexperienced purpose factors. These experiments are carried out within the Robotic Brokers Laboratory at School of Data Know-how of the Czech Technical College in Prague.
Firstly, every agent searches for a path individually. That is accomplished with the RRT* algorithm as talked about above. The ensuing path is then smoothed utilizing B-spline curves, polynomial piecewise curves utilized to vertices of the trail. This removes sharp turns and makes the trail simpler to traverse for a bodily agent.
Particular person paths are then despatched to the upper stage of the algorithm, wherein paths are in contrast and conflicts are discovered. Battle arises if two brokers (that are represented as inflexible round our bodies) overlap at any given time. If that’s the case, constraints are created to forbid one of many brokers from passing by way of the conflicting area at a time interval throughout which it was beforehand current in that area. Each choices which constrain one of many brokers are tried – a tree of potential constraint settings and their options is constructed and expanded upon with every battle discovered. When a brand new constraint is added, this info passes to all brokers it issues and their paths are re-planned in order that they keep away from the constrained time and area. Then the paths are checked once more for validity, and this repeats till a conflict-free resolution, which goals to be as quick as potential is discovered.
This manner, brokers can successfully transfer with out dropping velocity whereas turning and with out colliding with one another. Though there are environments corresponding to slender hallways the place slowing down and even stopping could also be vital for brokers to securely go, CE-CBS finds options in most environments.
This analysis is supported by the Czech Science Basis, 22-31346S.
You may learn our paper right here.
References
- Janovská, Okay. and Surynek, P. (2024). Multi-agent Path Discovering in Steady Atmosphere, CoRR.
- Sharon, G., Stern, R., Felner, A., and Sturtevant, N. R. (2014). Battle-based seek for optimum multi-agent pathfinding, Synthetic Intelligence.
- Karaman, S. and Frazzoli, E. (2011). Sampling-based algorithms for optimum movement planning, CoRR.
- Piegl, L. and Tiller, W. (1996). The NURBS Ebook, Springer-Verlag, New York, USA, second version.
- Silver, D. (2005). Cooperative pathfinding, Proceedings of the First Synthetic Intelligence and Interactive Digital Leisure Convention, Marina del Rey, California, USA.
AIhub
is a non-profit devoted to connecting the AI group to the general public by offering free, high-quality info in AI.

AIhub
is a non-profit devoted to connecting the AI group to the general public by offering free, high-quality info in AI.

